Are you scratching like crazy and wondering why you have eczema? Do you even have eczema? Let’s get straight to the point. Learn what really causes it and find out how to cure that itchy skin inflammation.
What Is Eczema?
Eczema is a kind of skin condition that makes the skin red, swollen and sore, with sometimes small bubbles filled with fluid (serum). Eczema is the main group of skin inflammations under which there are many subdivisions. To get a clearer picture, think about eczema as if it was a company. Let’s say GM (General Motors). GM is a car manufacturer that has many subsidiaries such as Chevrolet, Cadillac, Buick, GMC and many other brands. Eczema acts in a similar way. In the healthcare field, it is commonly known as a type of atopic dermatitis or simply skin inflammation as a general diagnosis. The name Eczema comes from Greek (ekzema or ekzein). In Greek, ek (the first part of the word) means “out”, while zein means “boil”. In other words, eczema could be translated as “skin flaring up”. As it is a very generic term, there are many kinds of eczemas. The most common medical terms that refer to this skin condition include Seborrheic dermatitis, Atopic Dermatitis, Nummular Dermatitis, Contact Dermatitis, Stasis Dermatitis.
So, if you are told you have eczema, ask to be specific to really know your skin condition so that you can choose the most effective treatment available.
What Causes Eczema?
To start with, it is important to mention that one of the reasons that causing eczema is a congestion of the lymphatic system, which happens frequently. The lymphatic system is a network of fluids in the body that makes sure that the inner body is cleaned up so that minerals and other substances can reach their destination and accomplish their functions. However, if the lymphatic system is congested, the body becomes vulnerable to internal aggressions such as bacteria, infections and other diseases (learn more about lymphatic system). As such, the body is permeable to skin inflammations like eczema.
Another explanation to why you have eczema is that you immune system might not be strong enough to defend itself against internal and eterneal infections. Weak immune system is one of the causes of many conditions such as frequent colds, fatigue, anxiety and other common problems (read more about how to get a strong immune system).
In probably most cases, eczema can be trigger by a yeast infection. It is a type of fungi that start growing under the skin and infect the rash area.
You can also get eczema from substances that can create allergic reactions such as pollens (those microscopic yellow grains in flowers), dust mites, domestic companions (cats and even dogs).
Workout exercises or any type of intense activities can also cause eczema, as they may include perspiration, which can irritate the skin, just like hot weather and humidity levels (whether it’s very humid or dry).
Products that enter in contact with the skin can lead to skin inflammation as well. Some substances your body is irritated from are commonly found in soaps, alcohol-based ingredients, household cleaning items, shampoos, conditioners, creams and other products in contact with the skin.
Foods can trigger atopic eczema because the body cannot process and digest them properly. It is the case with animal ingredients like meats, fish, dairy products, and eggs. Ingredients including gluten proteins such as bread and pasta. Grains and cereals, along with soy products can also develop eczema.
Stress is a psychological factor known for its capacity to release certain hormones that can create or worsen atopic dermatitis.
How Do You Know You Have Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema)
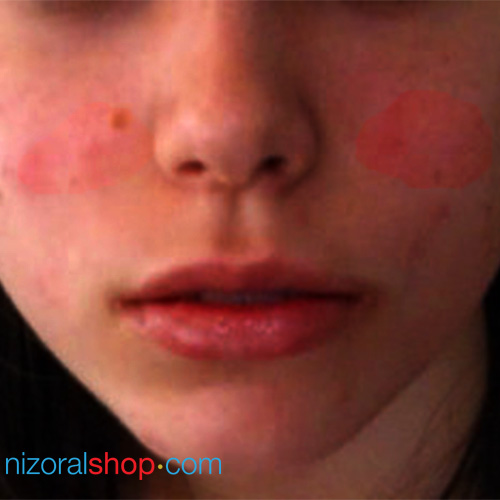
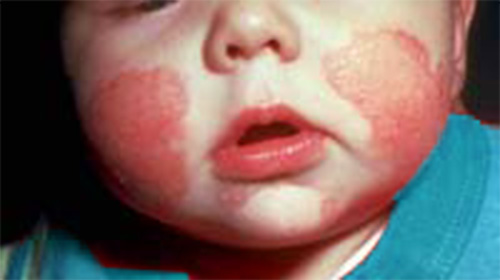
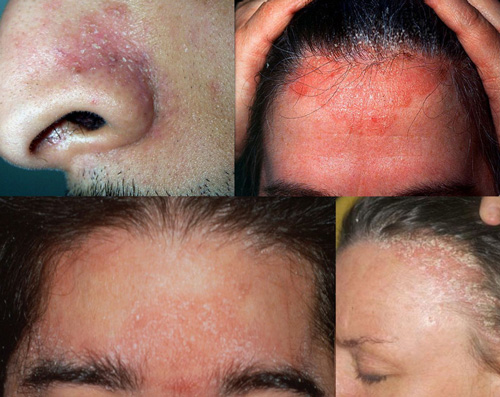
Eczema symptoms include rash red inflamed skin that may develop small blisters filled with serum. Eczema is almost always associated with dry and itchy skin. It is sometimes so intense that scratching the affected area may lead the skin to bleed, which worsens the condition, as it becomes more inflamed and sensitive. Other common factors indicating an eczema condition include swelling, colored patches and scaly areas.
See pictures below showing eczema:
Woman showing symptoms of eczema on face

Patient developing small blisters on the hand 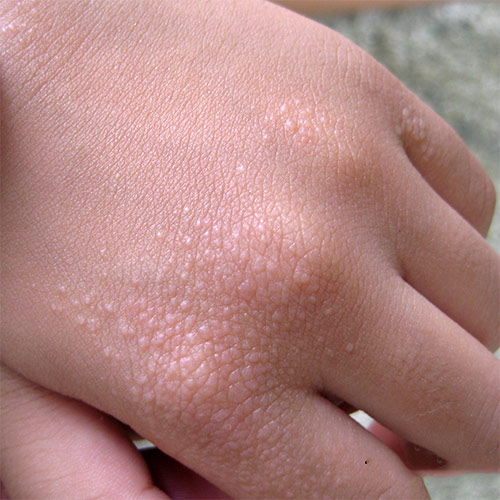
Nummular Eczema is characterized by coin shaped lesions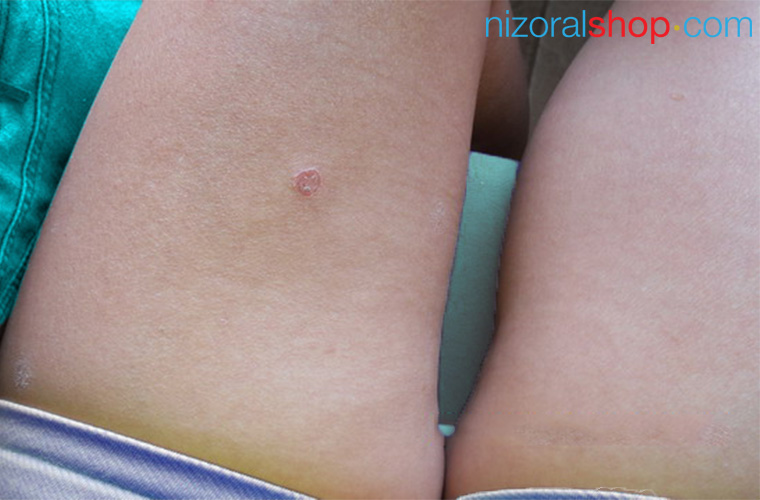
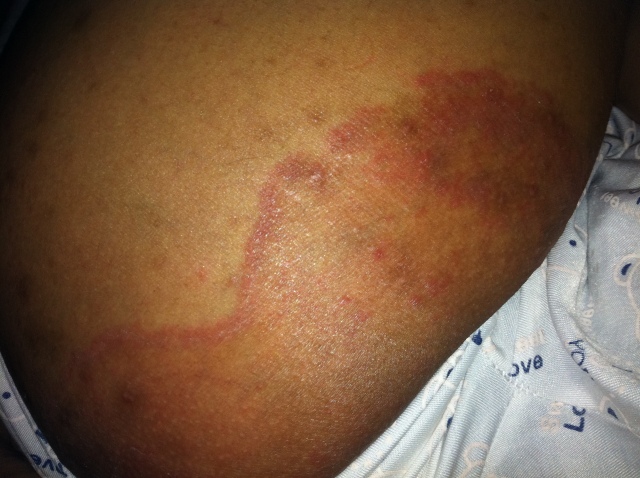
Woman suffering from Eczema on Legs (both thighs) red patches%20(1).jpg)
How To Get Rid Of Eczema?
There are a number of ways you can follow to treat eczema. A general advice is to take care of your skin when the moment you see eczema flaring up. For example, moisturizing the skin immediately after cleaning it, as it will act as a protective layer that nourishes and protects the skin. There are many moisturizing products out there that are natural remedies for eczema such as creams made from aloe-vera and coconut, which are natural ingredients calming skin inflammation. Wear cotton fabrics, as opposed to synthetic textiles that can irritate the skin. Avoid hot temperatures or activities that produce perspiration and humidity conditions. Other eczema natural treatments include to have a healthy diet primarily based on eating and juicing green vegetables as well as organic fruits that help cleanse your digestive system.
If natural remedies can’t seem to treat eczema, healthcare providers often prescribe topical treatments that can be found in cream or gel, which have Ketoconazole as a main active ingredient. As most eczema problems are dermatitis (yeast), ketoconazole focuses on eliminating fungi and yeasts that cause itchy rashes, redness, cracking, scaling and swelling. Nizoral Cream is a good example of prescription, as it contains enough Ketoconazole (2%) to treat the affected area. Click on Nizoral Cream to learn more how to cure eczema.
Related articles that may interest you:
Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. The material appearing on this page is for informational use only. It should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.



.jpg)

